



In the pursuit of sustainable and renewable energy sources, solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has emerged
as one of the most promising solutions to combat climate change and secure a greener future.
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, offering an environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional fossil-fuel-based energy generation.
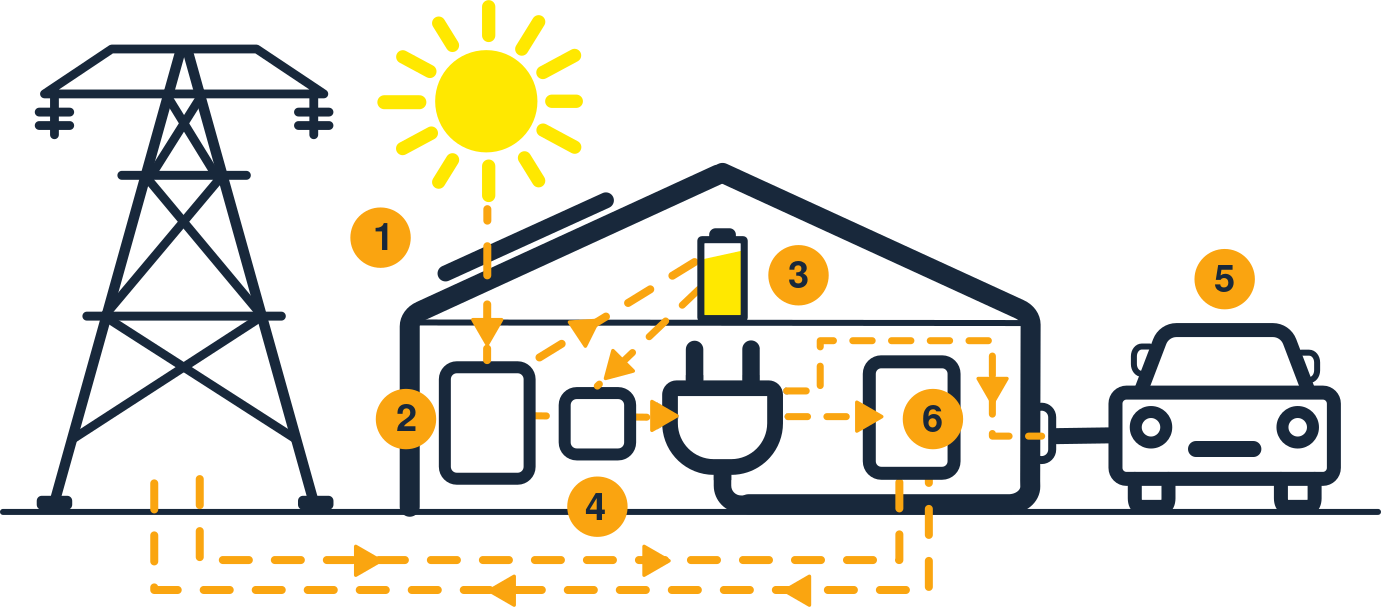
Solar PV’s success lies in its ability to tap into an abundant, clean, and inexhaustible source of energy: the sun. The process involves the use of photovoltaic cells, typically made from silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight and liberates electrons, generating an electric current. These cells are organised into modules, combining multiple modules to create solar panels. The panels can be installed on rooftops, in open fields, or integrated into building facades, making solar PV a versatile and scalable energy solution.
One of the key advantages of solar PV is its sustainability. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy production does not emit harmful greenhouse gases, contributing significantly to mitigating climate change and reducing our carbon footprint. As technology advances, solar PV’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness continue to improve, making it an increasingly attractive option for energy generation worldwide.
The adoption of solar PV has been rapidly growing across the globe. Governments and private sectors are investing in solar energy projects to meet renewable energy targets, bolster energy security, and create job opportunities in the clean energy sector. Moreover, individuals are increasingly embracing solar power to take control of their energy consumption, reduce electricity bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Beyond environmental and economic benefits, solar PV also promotes energy independence. Solar installations enhance grid resiliency and reduce the risk of widespread blackouts during emergencies or natural disasters by decentralising power generation and enabling local energy production
However, challenges remain for the widespread adoption of solar PV. Issues such as intermittency (the sun’s availability is dependent on time and weather), energy storage, and the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of solar panels require innovative solutions and ongoing research.
To Provide You The Best Solar Experience










Solar panel installation refers to the process of placing solar panels on a residential or commercial property to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. It involves mounting the panels on rooftops, carports, or ground-mounted structures.
Solar panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The panels are made up of multiple PV cells, which generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. An inverter then converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is used to power electrical devices in your home or business.
Most homes are suitable for solar panel installation, provided they have access to sunlight. Ideally, your roof or property should have a south-facing orientation with minimal shading. However, solar panels can still be installed on east- or west-facing roofs, although they may produce slightly less electricity.
The cost of solar panels can vary depending on factors such as the size of the system, the type of panels used, and the complexity of the installation. Generally, the cost includes the price of the panels, inverters, mounting equipment, installation labor, and any necessary permits. It’s best to obtain quotes from multiple solar installers to get an accurate estimate for your specific situation.
Solar panels are designed to be durable and long-lasting. Most panels come with a warranty that guarantees their performance for 20 to 25 years. However, solar panels can continue to produce electricity well beyond their warranty period, with many lasting 30 years or more.
Solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy or rainy days, although their output will be reduced compared to sunny days. While direct sunlight is ideal, solar panels can still produce a significant amount of power in diffused or indirect sunlight. Additionally, excess electricity generated during sunny days can be stored in batteries or fed back into the grid for later use.
While it’s technically possible to install solar panels yourself, it is generally recommended to hire a professional solar installer. Solar panel installation involves electrical work, knowledge of building codes and permits, and proper system design to maximize efficiency. A professional installer will ensure the panels are safely and correctly installed, comply with regulations, and may also assist with paperwork and permits.
Yes, solar panels can significantly reduce your electricity bills. By generating your own electricity, you rely less on the grid for power, resulting in lower monthly bills. The exact savings will depend on factors such as your energy consumption, the size of the solar system, and local electricity rates. In some cases, you may even generate excess electricity, which can be credited or sold back to your utility company.
Yes, there are various financial incentives available for solar panel installations in many countries. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, grants, and net metering programs. It’s advisable to research and consult with a local solar installer or energy authority to understand the incentives and subsidies available in your area.
Yes, it is often possible to add more solar panels to an existing system in the future. This depends on the design and capacity of your current system and the available space for additional panels. It’s best to consult with a solar professional to assess the feasibility and compatibility.
©2023 This website is the property of Solar4Good UK Ltd. The content of this website and the information contained therein informs the user of the services provided by Solar4Good UK.